Predeposition Equations
A predeposition diffusion is defined as a diffusion with an unlimited source of
impurities (in excess of that required to reach the solid solubility limit of the
substrate).
The distribution of the impurities within the substrate is found by solving Fick's
Laws with the following initial and boundary conditions:
Initial condition:
N(x=0+,t=0) = 0 (no impurity in the substrate at the start of the predep)
Boundary conditions:
N0 = constant = Nsl (surface concentration is limited by the
solid solubility)
N∞ = 0 (limited time so that impurity does not diffuse through the material)
The solution to Ficks Laws:
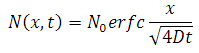
where:
N0 = Nsl (the surface concentration = solid solubility limit
of the dopant/substrate system)
x = position within the substrate where N is evaluated
D = diffusion coefficient of the impurity (temperature and dopant specific)
t = time of the diffusion
Dose (Q)
The dose is the # impurity atoms/cm2 and is found by integrating the
flux crossing the surface of the substrate over the length of the predep.
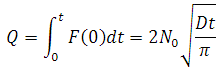
|